كل ما تحتاج لمعرفته حول البنزوديازيبينات
البنزوديازيبينات، المعروفة أيضًا باسم "البنزوس"، هي فئة من الأدوية تُوصف عادةً لعلاج القلق والأرق وبعض الحالات الطبية. ورغم فعاليتها العالية عند استخدامها على المدى القصير، إلا أنها تنطوي على مخاطر، منها الإدمان وأعراض الانسحاب. دعونا نوضح ماهية البنزوديازيبينات، وكيفية عملها، وما تحتاج إلى معرفته قبل تناولها.
ما هي البنزوديازيبينات؟
البنزوديازيبينات هي مجموعة من الأدوية التي تعمل كـ المهدئات أو المنومات أو مضادات القلق. يتم وصفها عادة لـ:
- تخفيف القلق أو نوبات الهلع على المدى القصير.
- أرق (مشاكل النوم).
- تشنجات العضلات.
- النوبات.
- أعراض انسحاب الكحول.
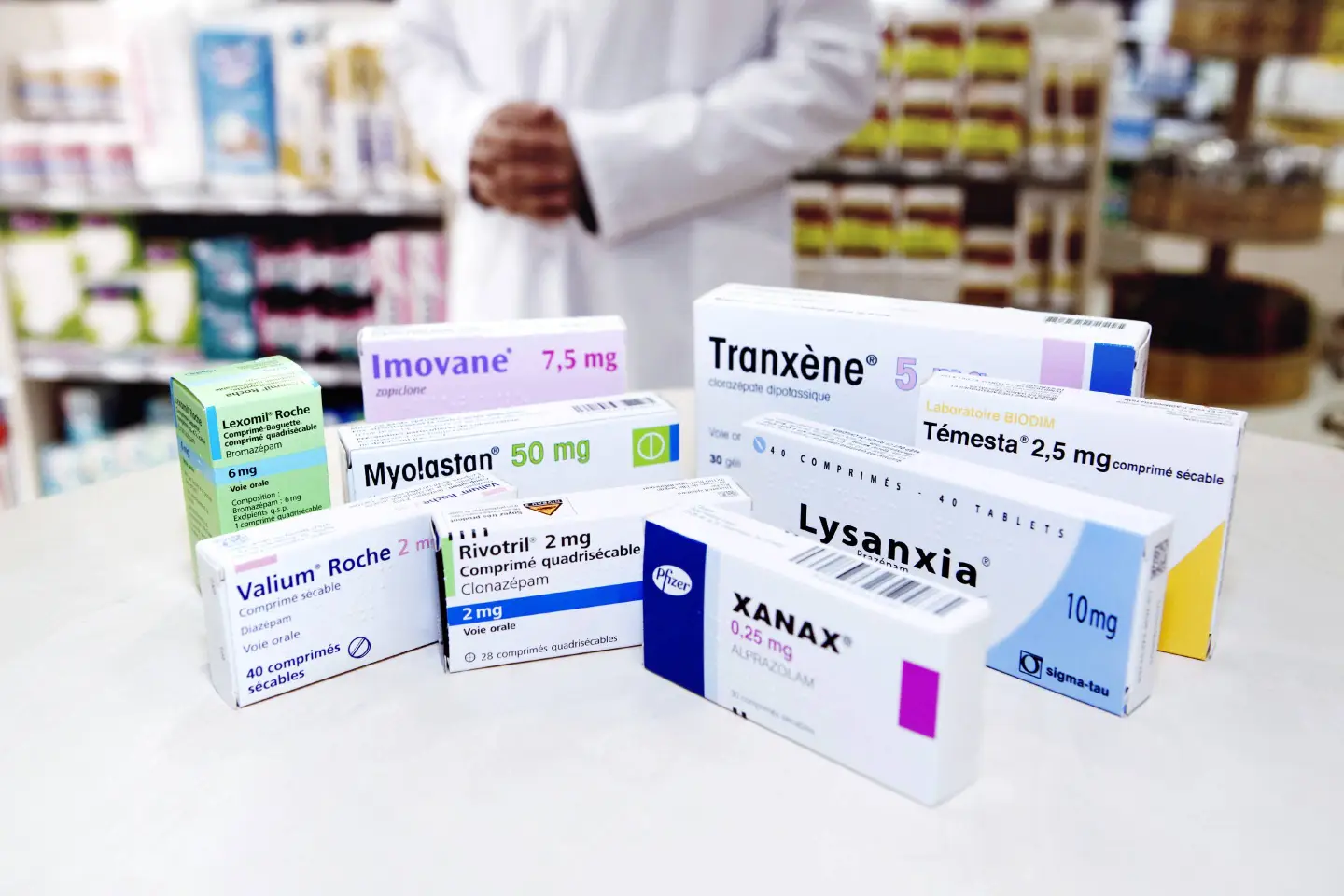
تشمل البنزوديازيبينات الشائعة ما يلي:
- ألبرازولام (زاناكس)
- ديازيبام (فاليوم)
- لورازيبام (أتيفان)
- كلونازيبام (كلونوبين)
- تيمازيبام (ريستوريل)
كيف تعمل البنزوديازيبينات؟
تعمل البنزوديازيبينات عن طريق تعزيز تأثيرات جابا، وهي مادة كيميائية في الدماغ تُهدئ النشاط العصبي. ترتبط بمستقبلات محددة في الدماغ (مستقبلات GABA-A)، مما يزيد من قدرة GABA على تقليل القلق، وتعزيز الاسترخاء، وتحفيز النوم.
ما هي استخدامات البنزوديازيبينات؟
تشمل الاستخدامات المعتمدة من قبل إدارة الغذاء والدواء ما يلي:

- اضطرابات القلق (على سبيل المثال، اضطراب القلق العام، اضطراب الهلع).
- أرق (علاج قصير المدى).
- اضطرابات النوبات.
- تشنجات العضلات.
- انسحاب الكحول.
تشمل الاستخدامات خارج العلامة ما يلي:
- الجمود (حالة نفسية خطيرة).
- الانفعال في حالات الطوارئ النفسية.
- التخدير قبل الجراحة.
من يجب عليه تجنب البنزوديازيبينات؟
البنزوديازيبينات ليست مناسبة للجميع. تجنبها أو استخدمها بحذر إذا كنت:
- لديك تاريخ من تعاطي المخدرات (خطر الاعتماد العالي).
- انت حامل أو مرضعة (قد يؤذي الطفل).
- لديك أمراض الكبد أو الكلى الشديدة (قد تحتاج إلى تعديل الجرعة).
- لديك انقطاع النفس النومي (قد يؤدي إلى تفاقم مشاكل التنفس).
- انت كبير (زيادة خطر السقوط والارتباك).
ما هي الآثار الجانبية؟
الآثار الجانبية الشائعة:
- النعاس أو التعب.
- الدوخة أو الدوار.
- الارتباك أو مشاكل الذاكرة.
- كلام غير واضح.
- ضعف العضلات.
الآثار الجانبية النادرة ولكن الخطيرة:
- ردود الفعل المتناقضة (على سبيل المثال، زيادة القلق، والعدوان).
- ردود الفعل التحسسية الشديدة (طفح جلدي، تورم، صعوبة في التنفس).
- الاكتئاب التنفسي (تنفس بطيء بشكل خطير، وخاصة مع المواد الأفيونية).
- أعراض الاعتماد والانسحاب (إذا توقفت فجأة).
مخاطر الاستخدام طويل الأمد
في حين أن البنزوديازيبينات فعالة للاستخدام على المدى القصير، إلا أن استخدامها على المدى الطويل يمكن أن يؤدي إلى:
- التحمل تحتاج إلى جرعات أعلى للحصول على نفس التأثير.
- الاعتماد: الاعتماد الجسدي أو النفسي على الدواء.
- أعراض الانسحاب: القلق والأرق والنوبات وغيرها إذا توقفت فجأة.
- التدهور المعرفي: مشاكل في الذاكرة وانخفاض حدة الذهن.
كيفية تناول البنزوديازيبينات بأمان
- اتبع تعليمات طبيبك: لا تأخذ أكثر من الجرعة الموصوفة.
- استخدم على المدى القصير: لا ينصح عمومًا باستخدام البنزوديازيبينات على المدى الطويل.
- تجنب الكحول والمهدئات الأخرى: يمكن أن تزيد من الآثار الجانبية مثل النعاس والاكتئاب التنفسي.
- لا تتوقف فجأة: يجب دائمًا تقليل الجرعة تحت إشراف طبي لتجنب أعراض الانسحاب.
الانسحاب والتوقف
قد يؤدي التوقف المفاجئ عن تناول البنزوديازيبينات إلى ظهور أعراض انسحاب شديدة، بما في ذلك:
- القلق الارتدادي أو الأرق.
- ارتعاش أو نوبات.
- التعرق، والغثيان، أو القيء.
- الهلوسة أو الارتباك.
لإيقاف البنزوديازيبينات بأمان:
- العمل مع طبيبك لإنشاء خطة التناقص التدريجي.
- قم بتقليل الجرعة تدريجيًا على مدى أسابيع أو أشهر.
- اطلب الدعم لإدارة أعراض الانسحاب.
التفاعلات الدوائية التي يجب تجنبها
يمكن أن تتفاعل البنزوديازيبينات مع أدوية أخرى، بما في ذلك:
- المواد الأفيونية (على سبيل المثال، المورفين، أوكسيكودون): زيادة خطر الاكتئاب التنفسي.
- الكحول: قد يؤدي إلى تفاقم التخدير والدوخة.
- مضادات الاكتئاب أو مضادات الذهان: قد تزيد من الآثار الجانبية.
- أدوية النوم (أدوية Z): يمكن أن يعزز التأثيرات المهدئة.
البنزوديازيبينات مقابل أدوية Z
أدوية Z (على سبيل المثال، زولبيديم, زوبيكلون) تُشبه البنزوديازيبينات، وتُوصف عادةً لعلاج الأرق. ورغم تأثيرها على مستقبلات الدماغ نفسها، إلا أنها أكثر انتقائية وقد تكون آثارها الجانبية أقل. ومع ذلك، فإنها لا تزال تحمل مخاطر الإدمان وأعراض الانسحاب.
الأفكار النهائية
قد تكون البنزوديازيبينات أداةً مفيدةً في علاج القلق والأرق وحالاتٍ أخرى، ولكنها ليست حلاًّ طويل الأمد. استخدمها دائمًا تحت إشرافٍ طبيٍّ دقيق، وكن على درايةٍ بمخاطر الاعتماد عليها وأعراض الانسحاب. إذا كنت تفكر في استخدام البنزوديازيبينات، فاستشر طبيبكَ لمعرفة مدى ملاءمتها لك، واستكشف علاجاتٍ بديلة، مثل العلاج النفسي أو تغييرات نمط الحياة.
إخلاء مسؤولية: هذه المقالة لأغراض إعلامية فقط. استشر طبيبك دائمًا قبل بدء تناول الأدوية أو إيقافها أو تغييرها.